What is Diabetes? Write its types/causes/symptoms/diagnosis?
Overview
Diabetes refers to a group of diseases that affect the body’s glucose. Diabetes is a disease that involves a mess with insulin. It is a very severe and chronic condition in which the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. Normally, the pancreas produces insulin, which the body stores and then uses. The body’s muscles and tissues use glucose, a vital form.
It affects millions of people. Diabetes affects 38.4 million people worldwide. And almost 8.7 million people are unaware of it. It was the leading cause of death. [1]
It is not because of eating too much sugar; it is because the body handles too much sugar in the blood. If the body is unable to handle sugar in the blood, it causes serious body issues. It affects almost 590 million people under the age of 20, which is almost 10% of the population. [2]
Types of Diabetes
Several types of diabetes exist, including:
- Type-1 Diabetes
- Type-2 Diabetes
- Prediabetes
- Gestational Diabetes
What is Type-1 Diabetes?
The immune system attacks type-1 diabetes, a chronic condition. The pancreas produces beta cells, which the immune system attacks. These cells produce insulin and maintain the sugar level in the blood.
Type 1 diabetes can be caused by genetic, environmental, or exposure to virus factors. Despite extensive research, the cause of this autoimmune condition, which damages the cells in the pancreas, remains unknown. They require insulin injections to maintain control.
Type-1 diabetes is also known as juvenile diabetes because its onset starts at the age of 20. It can cause serious emergencies when the sugar level in the blood is too high. This condition is known as diabetic ketoacidosis.
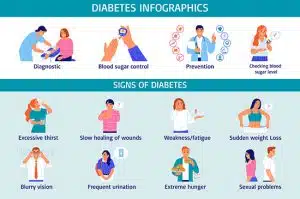
When we have type 1 diabetes, the symptoms include:
- Weight loss.
- Urination
- Feeling thirsty
- Blurry vision
- Mood swings
- Nausea
- Red-fleshed cheeks
- Abdominal pain
- Difficulty breathing
What is Type-2 Diabetes?
Type-2 diabetes is a condition that develops when your body does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin in the body. In this condition, the body cells do not even respond to the body’s insulin.
This causes the sugar to stay in the blood, resulting in a condition known as hyperglycemia, a higher cause of blood sugar levels. In this body, cells do not respond to insulin. It is linked to certain environmental factors, such as dietary conditions, obesity, and so on.
People with type-2 diabetes often go years without receiving a diagnosis because they don’t initially exhibit any symptoms.
- Cuts heal slowly.
- Tiredness
- Hunger
- Tingling in the hands
Prediabetes
In this case, your blood sugar level is higher than normal, which is high enough to meet type 2 requirements. This is known as pre-diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs during the months of pregnancy in mostly females because it reduces the level of glucose in the body.
Risk factors for diabetes
- Inactivity
- Weight
- Family history
Complications of diabetes
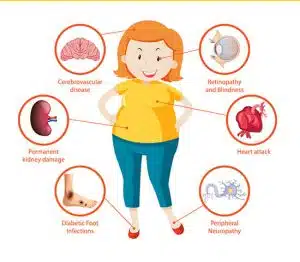
- Cardiovascular disease
- Neuropathy (Blood vessel damage)
- Retinopathy (Eye disorders)
- Kidney damage
- Slow healing from cuts
Diagnosis of Diabetes
Diabetes is diagnosed using a variety of methods; a blood sample is taken in the laboratory and prescribed by our healthcare practitioner. Here are the following tests for diabetes:
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Non-fasting glucose test
- Glycated haemoglobin
- Fasting glucose test

